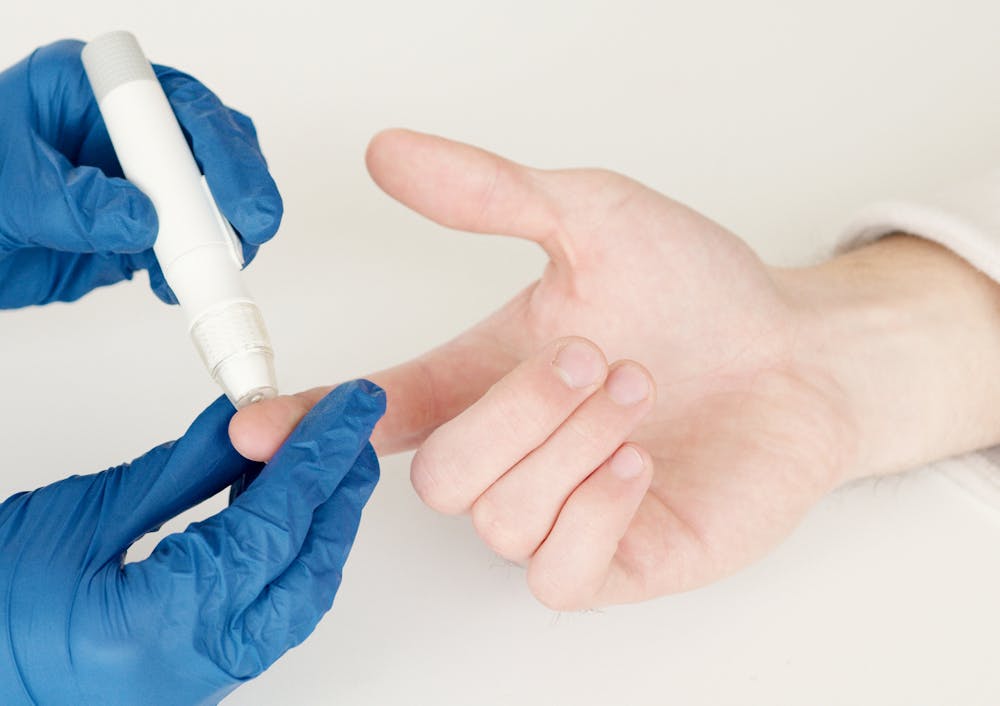
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. It helps individuals with diabetes make informed diet, exercise, and medication decisions. Regular monitoring can prevent complications and improve overall quality of life. This article explores the best practices for monitoring blood sugar levels and the tools available to help you stay on track.
Understanding Blood Sugar Monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring involves regularly checking the concentration of glucose in your blood. This practice is essential for people with diabetes to manage their condition effectively. By understanding how different activities, foods, and medications affect your blood sugar, you can make better lifestyle choices and adjust your diabetes management plan accordingly.
Why Monitoring is Important
Regular blood sugar monitoring helps prevent both short-term and long-term complications of diabetes. It enables you to detect hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) early, allowing you to take corrective actions promptly. Over time, consistent monitoring helps maintain blood sugar levels within the target range, reducing the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Types of Diabetes and Monitoring Needs
- Type 1 Diabetes: Requires frequent monitoring, often multiple times a day, to manage insulin therapy effectively.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Monitoring frequency varies depending on the treatment plan. Those on insulin may need to test more often than those managing their condition with diet and oral medications.
- Gestational Diabetes: Monitoring is crucial for managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby.
Best Practices for Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Consistent blood sugar testing is vital for effective diabetes management. The testing frequency depends on the type of diabetes and the individual’s treatment plan.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Testing is typically done before meals, at bedtime, and sometimes at night.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Testing may be done less frequently, depending on the treatment regimen.
- Gestational Diabetes: Often requires testing after meals to ensure levels remain within a healthy range.
Keeping a Log
Recording your blood sugar levels helps identify patterns and trends. You can maintain this log on paper, mobile apps, or digital tools.
- Paper Logs: Simple and accessible but may not provide detailed analysis.
- Apps and Digital Tools: Offer advanced features like trend analysis, integration with other health data, and easy sharing with healthcare providers.
Understanding Patterns
Identifying trends in your blood sugar levels helps you understand how different factors affect your condition.
- Recognizing Triggers: Certain foods, activities, stress, and illnesses can impact your blood sugar. Noting these triggers helps in managing them effectively.
- Adjusting Management Plan: Use the data to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication adjustments.
Setting Goals
Work with your healthcare provider to set personalized blood sugar targets. These goals help guide your daily management practices.
- A1C Goals: Aim for an A1C level that reflects good long-term glucose control, typically below 7% for many adults with diabetes.
- Daily Targets: Set realistic and attainable blood sugar goals for different times of the day, such as pre-meal and post-meal targets.
Responding to Readings
Knowing how to respond to your blood sugar readings is crucial.
- Immediate Actions: Learn how to treat high and low blood sugar levels. For hypoglycemia, consuming quick-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets or juice is essential. Adjusting insulin or oral medication as per your doctor’s advice is necessary for hyperglycemia.
- Long-Term Adjustments: Based on your monitoring data, you might need to make long-term changes to your diet, exercise routine, or medication.
Tools for Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Glucometers are traditional blood sugar meters that measure glucose levels using a small blood sample from a finger prick.
- How They Work: Place a drop of blood on a test strip inserted into the meter, then display your blood sugar level.
- Features to Consider: Look for accuracy, ease of use, memory storage, and cost of test strips.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs provide real-time blood sugar readings and trends throughout the day and night.
- How They Work: A small sensor inserted under the skin continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. Data is transmitted to a display device.
- Advantages: It offers trend analysis, reduces the need for finger pricks, and provides alerts for high and low blood sugar levels.
Wearables and Smart Devices
Wearables like smartwatches and fitness trackers can also play a role in diabetes management.
- Examples: Devices like the Apple Watch and Fitbit can track physical activity and heart rate and even integrate with health apps for comprehensive data management.
- Benefits: These devices offer convenience, continuous monitoring, and valuable health insights to manage diabetes.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Tools
Selecting the right tools depends on your individual needs and lifestyle.
- Lifestyle Considerations: Consider your activity level, work schedule, and personal preferences when choosing a monitoring tool.
- Ease of Use: Opt for devices that fit seamlessly into your daily routine and are easy to use.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Seek professional advice when selecting blood sugar monitoring tools.
- Recommendations: Your healthcare provider can suggest tools best suit your condition and management plan.
- Insurance and Cost: Understand the coverage and affordability of different monitoring tools. Many insurance plans cover the cost of glucometers and CGMs.
Trying Multiple Tools
Experiment with different devices to find the best fit.
- Testing Different Devices: Evaluate various tools’ comfort, convenience, and accuracy.
- Adjusting as Needed: Be flexible and open to changing tools to improve your monitoring experience.
Conclusion
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management. By following best practices and utilizing the right tools, you can maintain better control over your condition and improve your overall health. Consult with your healthcare provider to personalize your monitoring strategy and explore various tools to find what works best for you. For those looking to enhance their management plan, consider options to buy Mounjaro online as part of a comprehensive approach to diabetes care.